Why Is Diamond An Insulator: Exploring Its Electrical Properties
Why Diamond Behaves Like An Insulator?
Keywords searched by users: Why is diamond an insulator is diamond a conductor or insulator of heat, is graphite an insulator, is oil a conductor or insulator, is lemon juice an insulator or conductor, is glass a conductor or insulator, is ebonite an insulator, dry wood insulator, is oil an insulator
Is Diamond An Insulator?
Is diamond a good conductor of electricity? No, it’s actually the opposite. Unlike metals, which conduct electricity well, diamond falls into the category of electrical insulators. This classification implies that electric current does not readily flow through diamond. This distinct behavior is a result of diamond’s particular crystal structure and how its carbon atoms are arranged. Understanding this unique structure helps explain why diamond possesses insulating properties, distinguishing it from conductive metals.
Why Is Diamond An Insulator And Graphite A Conductor?
The differing electrical conductivity of diamond and graphite can be attributed to their distinct molecular structures and electronic configurations. In the molecular structure of graphite, each carbon atom has one valence electron that remains unbound, allowing for easy movement within the material, thereby facilitating its role as a proficient electrical conductor. Conversely, in the crystal lattice of diamond, carbon atoms are fully bonded and lack free mobile electrons, resulting in poor electrical conductivity for diamond. This stark contrast in electronic mobility elucidates why graphite conducts electricity effectively, while diamond acts as an insulator.
Why Diamond Is A Hard And Electrical Insulator?
Diamond possesses exceptional hardness and acts as an effective electrical insulator due to its unique atomic structure. In a diamond crystal, each carbon atom forms strong covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms, creating a tightly bound lattice structure. Consequently, this configuration results in the absence of free electrons within the diamond’s atomic arrangement. Since there are no free electrons available for electrical conduction, diamond exhibits poor electrical conductivity, making it an excellent insulator against electrical currents. This exceptional hardness and insulating property stem from the strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms in the diamond lattice, which tightly hold the atoms in place and prevent the flow of electrons.
Top 7 Why is diamond an insulator




Categories: Summary 58 Why Is Diamond An Insulator
See more here: cayxanhthanglong.net
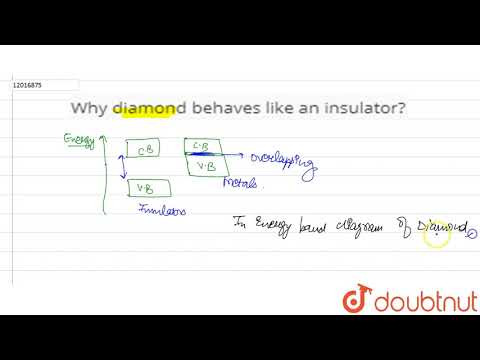
In a diamond, all the four electrons present in the outer shell on each carbon atom are used in covalent bonding, so there are no delocalised electrons present and thus makes the diamond an insulator.Unlike metals that are good conductors of electricity, diamond is classified as an electrical insulator. This means that it does not allow the flow of electric current through it easily. The reason behind diamond’s insulating properties lies in its unique crystal structure and the arrangement of its carbon atoms.In a graphite molecule, one valence electron of each carbon atom remains free, Thus making graphite a good conductor of electricity. Whereas In diamond, they have no free mobile electron. That is why diamond are bad conductor electricity.
Learn more about the topic Why is diamond an insulator.
- Is diamond an insulator?
- Is Diamond Insulator? 5 Facts You Should Know! –
- Why is graphite a good conductor of electricity but not diamond? – Toppr
- Why is diamond a bad conductor of electricity? – BYJU’S
- Diamond is not good conductor of electricity because – BYJU’S
- Diamond is a bad conductor of electricity but a good … – Toppr
See more: https://cayxanhthanglong.net/category/social-media
